| Description |
| Operation |
| Design and Development |
[24-AUG-25] A BCAM or Boston CCD Angle Monitor, pronounced "beecam", is an optical survey instrument that incorporates both cameras and light sources. The H-BCAM Head (A3025) is a Long-Wire Data Acquisition (LWDAQ) Device that reads out two ICX424 image sensors and drives six light sources. When the A3025 is connected to a pair of H-BCAM Side Heads (A3026), these light sources are four laser diodes in 5.6-mm metal packages, such as the ADL65074TL1, and two arrays of four LEDs in 3-mm plastic packages, such as the VLHW4100. The laser diodes act as point sources for other BCAMs to view, or for the BCAM itself to view in retroreflecting targets. The white LEDs illuminate distributed retroreflecting targest for the BCAM to view itself. The image sensor readout is identical to that of the Camera Head (A2075A), except that the A3025 provides readout of two image sensors. When the A3025 is connected to two ICX424 Minimal Heads (A2076), it presents the two image sensors as LWDAQ device elements one and two.
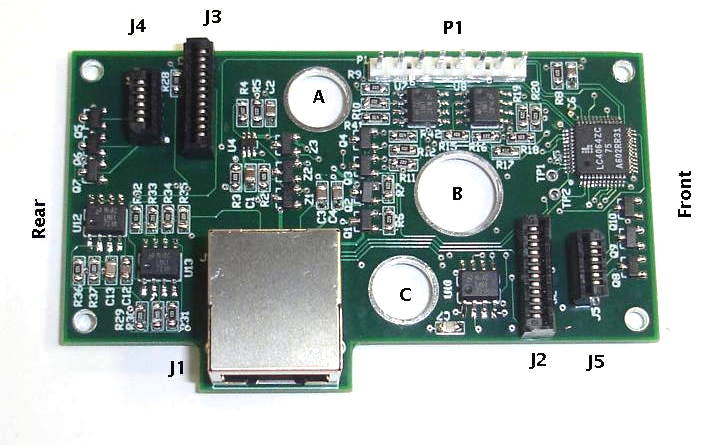
We designed the A3025A and A3025B for use in the Black and Blue H-BCAM respectively (H-BCAM is pronounced "h-beecam"). The H-BCAM was first conceived for the HIE-ISOLDE Alignment System, hence the use of the letter "H" in its name. The A3025B is a mirror image of the A3025A. Both circuits have amplifier gain chosen for use with the ICX424's single-pixel readout, as we discuss here. For quadruple-pixel readout, we reduce the gain of the output amplifiers by a factor of three so that the higher saturation voltage of the quadruple pixel will fall within the dynamic range of the converter on the LWDAQ Driver (we set R31 and R32 to 390 Ω).
| Version | Description |
|---|---|
| 3025A | Black H-BCAM Head (Optimized for Single-Pixel Readout) |
| 3025B | Blue H-BCAM Head (Optimized for Single-Pixel Readout) |
| 3025C | Black H-BCAM Head (Optimized for Quadruple-Pixel Readout) |
| 3025D | Blue H-BCAM Head (Optimized for Quadruple-Pixel Readout) |
The quadruple-pixel readout is four times faster than the single-pixel readout, because the A3025 bins blocks of four pixels together, so there are four times fewer of them to be read out by the LWDAQ Driver. The faster readout makes for faster data acquisition. Our experiments suggest that BCAM precision with single-pixel readout is 0.2 μm rms on the image sensor, and 0.3 μm for quadruple-pixel readout. For most BCAM applications, this degredation is insignificant. Furthermore, when the ICX424 image sensor has been irradiated by fast neutrons, its dark current increases. By binning four pixels together, we of course bin four times as much dark current into one pixel, which exactly balances the fact that the readout speed is four times faster, so that the net dark current per pixel remains the same. But it turns out that, in the ICX424, the saturation level of the quadruple pixel is three times higher than the saturation level of one pixel. As a result, we can tolerate three times as much neutron damage with quadruple-pixel readout as with single-pixel readout.
Due to an oversight on our part, the orientation of the six-way flex sockets on the A3025L/R are compatible with the A3026L/R H-BCAM Side Heads, but not the A2074C/E N-BCAM Laser Heads. If we want to use the A2074C/D with the A3025L/R, we must remove and rotate the six-way flex sockets on either the A2074C/D or A3025L/R.
[24-SEP-25] The A3025 is a LWDAQ Device, meeting all requirements of the LWDAQ Specification. The allocation of its sixteen command bits is consistent with other ICX424AL devices.
| DC16 | DC15 | DC14 | DC13 | DC12 | DC11 | DC10 | DC9 | DC8 | DC7 | DC6 | DC5 | DC4 | DC3 | DC2 | DC1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PXBN | ON6 | ON5 | ON4 | ON3 | ON2 | ON1 | CCD1 | WAKE | LB | SUB | V3 | V2 | V1 | H | RDP |
Note that the commmand bits are numbered 1-16, nor 0-15. When we describe the state of the bits with a four-digit hexadecimal number, the top bit is DC16 and the bottom bit is DC1. There is no DC0. We can set the command bits on an A3025 by transmitting a sixteen-bit device command using the LWDAQ Diagnostic Instrument. To turn on the two front-face lasers, for example, we use device command 0x1880, because this command sets DC13, DC12, and DC8, which are ON4, ON3, and WAKE respectively. To turn on the rear LED array we use 0x2080. In the Diagnostic Instrument, we enter the four hexadecimal digits in the Command (Hex) entry box, point the instrument at our BCAM Head (A3025) and press Transmit.
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| 0x1880 | Turn on both front face lasers. |
| 0x4080 | Turn on front face LEDs. |
| 0x0380 | Turn on both rear face lasers. |
| 0x2080 | Turn on rear face LEDs. |
Bits ON1-ON6 turn on sources 1-6. Sources 1, 2, and 5 are connected to J4, and sources 3, 4, and 6 are connected to J5, as shown in the schematic. Both J4 and J5 are 6-way 1-mm pitch flex connectors. The allocation of sources to the connector pins is compatible with the Polar BCAM Head and Azimuthal BCAM Head, in which two laser sources were driven through each six-way connector. In the H-BCAM, we add one LED array to each of two six-way connectors, and call these sources 5 and 6. The CCD1 bit selects the first of two image sensors available on the A3025.
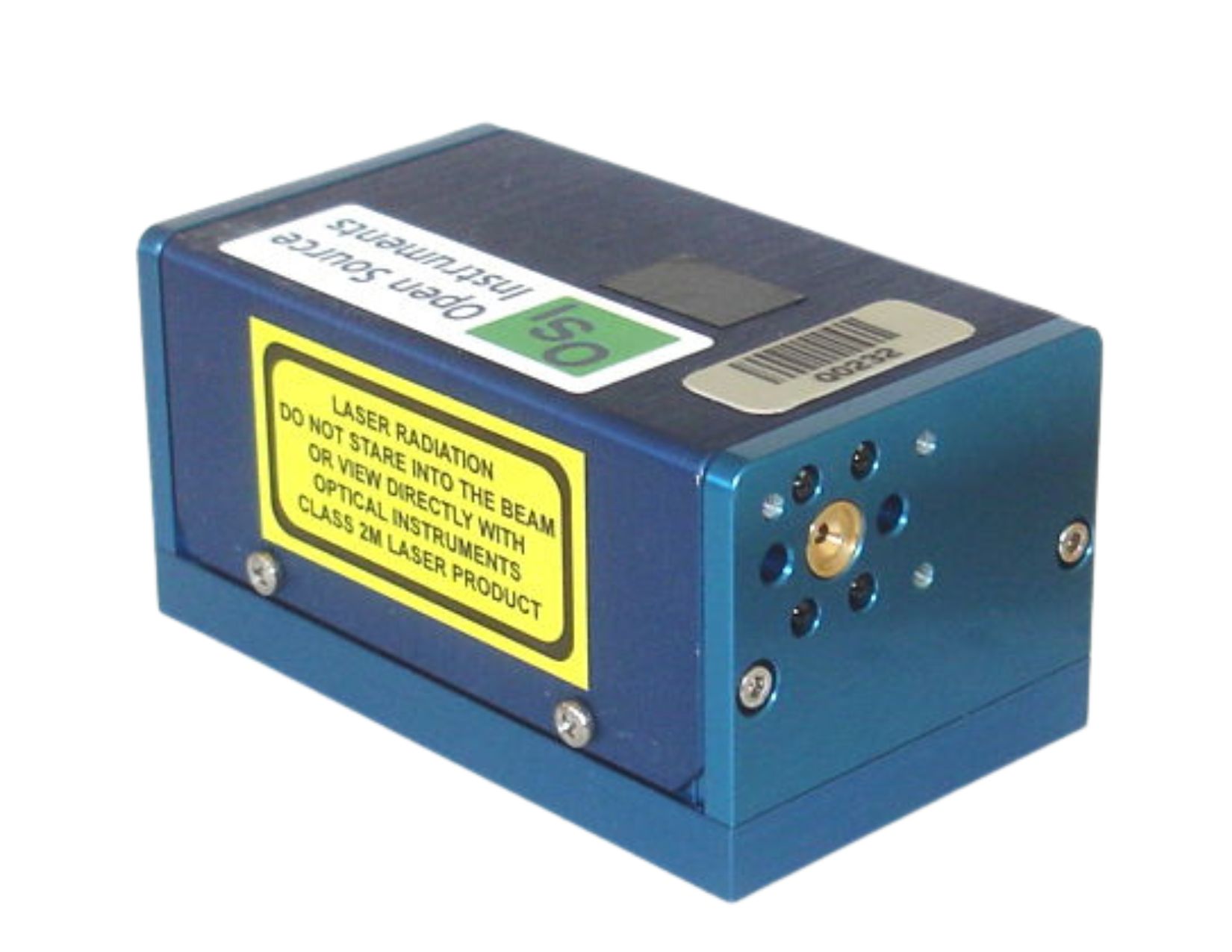
The SUB bit applies a pulse to the substrate of the image sensors so as to clear their image areas of charge. The V1-V3 bits control the levels of the vertical clock phases of the image sensors. The LWDAQ Driver controls the vertical clock phases directly during image readout by transmitting LWDAQ commands. The H bit enables the image sensor horizontal clocks, so that subsequent LWDAQ stop bits cause pulses on the clocks. The RDP, combined with V1 and V2 asserted, applies a read pulse to the image sensors, which transfers the image area charge into the transfer array. The PXBN bit is for pixel binning, which selects the quadruple-pixel readout. The LWDAQ Driver is responsible for combining rows of pixels through its manipulation of V1-V3 and H, but the A3025 is responsible for combining pixel columns, which it does with a double-pulse on the image sensor horizontal clock inputs. For more information on capturing images from the ICX424, see the Camera Head (A2075). The A3025 is intended for use in the H-BCAM. The H-BCAM is the first BCAM to use the ICX424 image sensor, and the first to provide an LED flash for illuminating retroreflecting targets in its field of view. The figure below shows the black H-BCAM.

The front face of the H-BCAM presents seven circular apertures. One aperture contains the brass lens-holder for the front-facing camera. The apertures on the left and right of the lens are for laser diodes. The other four holes above and below are for white LEDs. The numbering of the four lasers is the same as for the Polar BCAMs, see here. Looking at the front face of the Black H-BCAM, Source 3 (ON3) is on the left and Source 4 (ON4) is on the right. Looking at the rear face of the Black H-BCAM, Source 1 (ON1) is on the left and Source 2 (ON2) is on the right. Source 6 is the array of four LEDs on the front face and Source 5 is the array of four LEDs on the rear face. On the Blue H-BCAM, the front-face has Source 3 (ON3) on the right and Source 4 (ON4) on the left, while the rear face has Source 1 (ON1) on the right and Source 2 (ON2) on the left.

The following figure shows the interior of a Black H-BCAM. The circuit board screwed to the base of the chassis is a Black BCAM Head (A3025A). On the front and rear walls are two Black H-BCAM Side Heads (A3026A). The image sensors are mounted on ICX424 Minimal Heads (A2076D).
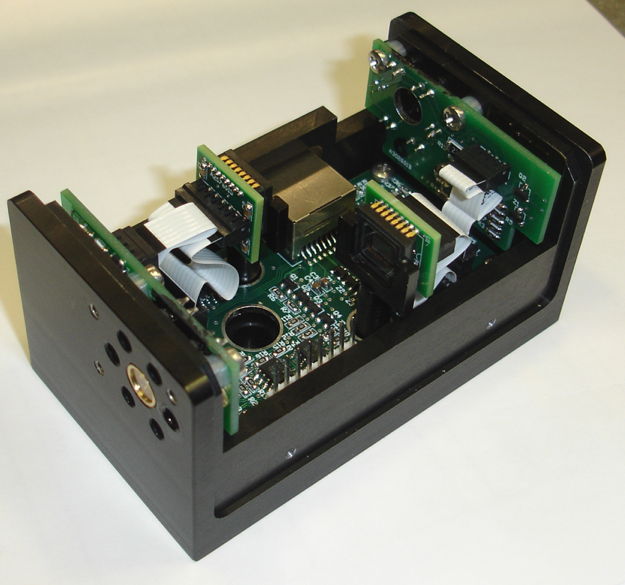

The two image sensors are glued into U-brackets, which are in turn supported by posts that are screwed to the base of the chassis. In order to replace the A3025 circuit, we must remove the two posts and the two A3026 circuits. Thus replacement of the A3025 requires re-calibration of both cameras and all four lasers. The A2076Ds connect to the A3025A with two 50-mm, 6-way flex cables. The two A2076Ds connect to the A3025A with two 50-mm, 12-way flex cables. The A3025 can operate with only one image sensor connected, provided that image sensor is CCD2 (J3, front-facing camera). If we connect only CCD1 (J2, rear-facing camera), the image is dim and negated. The A3025 can operate with flex cables up to 300 mm provided both image sensors are plugged in. For more details see below.
[24-SEP-25] For design files and development logbook, see the A3025 design and development page at D3025.